What are fibroids and what are the symptoms?
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are non cancerous tumors of the womb or uterus. These tumors start in the myometrium (muscle) of the uterus. Fibroids occur in more than 25% of women in the reproductive age group: 20 – 50 yrs.
The symptoms are usually excessive bleeding and pain during periods, heaviness in lower abdomen, inability to conceive, and if the fibroid is large , then lump in the abdomen and difficulty in passing urine and constipation.
How are fibroids managed?
Medications for uterine fibroids don’t eliminate fibroids, but shrink them in size .Medications called Gn-RH agonists put patients into a temporary menopausal state. As a result, menstruation stops, fibroids shrink and anemia often improves. They typically are used for no more than three to six months because of severe side effects. Ulipristal acetate is a steroid that reversibly binds to the progesterone receptor and modulates its activity. It controls fibroid related symptoms by reducing fibroid size.
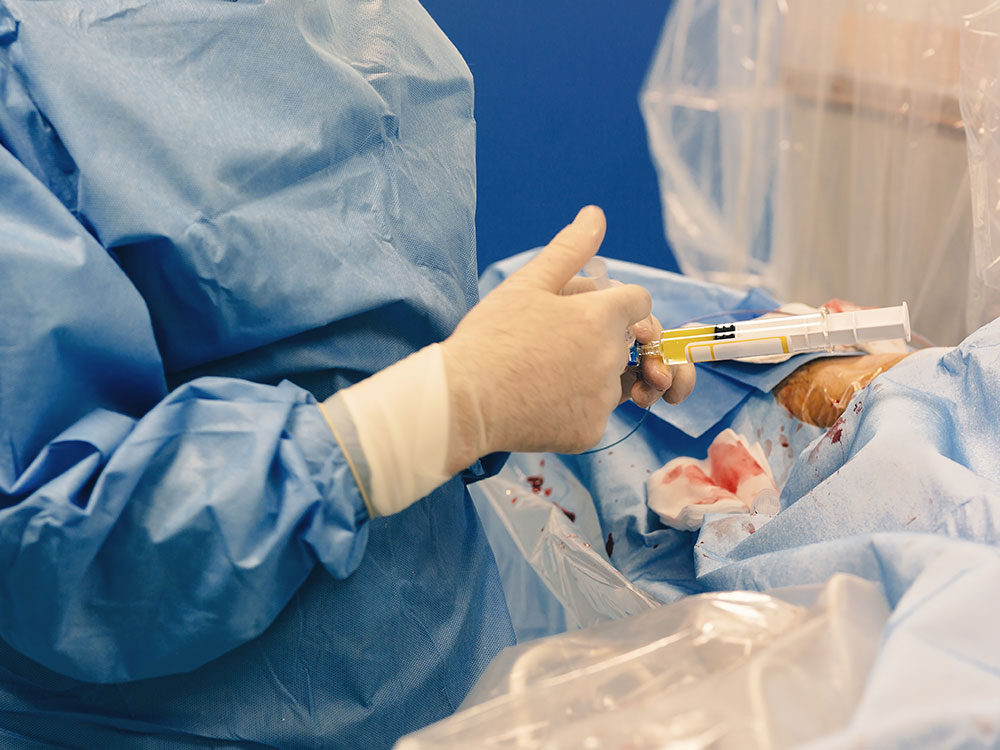
MRI-guided focused ultrasound is a non-invasive treatment option for reducing fibroid size. It is Performed inside an MRI scanner. The ultrasound transducer focuses sound waves (sonications) into the fibroid to heat and destroy small areas of fibroid tissue. Uterine artery embolization : Small particles (embolic agents) are injected into the arteries supplying the uterus, cutting off blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink and die. Complications may occur if the blood supply to your ovaries or other organs is compromised.